
Industrial vision systems in robotics, surveillance, transportation, and smart city projects depend heavily on reliable image sensors that deliver consistent performance across a wide range of lighting conditions. Among the many available options, the Sony 1/2" IMX385 STARVIS night vision USB camera module has quickly become a top choice for engineers and developers designing embedded vision systems.
Equipped with starlight-level low-light imaging, flexible lens options (6mm / 8mm / 2.8mm starlight lens), and the possibility to add a metal case for durability, this camera module addresses the critical questions engineers ask when integrating imaging hardware into real-world systems.
This article examines the five most common questions and highest-priority needs of engineers and developers when considering the IMX385 sensor, and provides expert technical answers with practical recommendations.
The IMX385 low light performance is widely regarded as its core advantage. Built with Sony STARVIS back-illuminated pixel technology, the sensor is optimized to deliver full-color imaging in conditions as dim as starlight or moonlight.
Why it matters: For engineers designing smart surveillance systems in the U.S. or Europe, the ability to capture high-quality imagery in near-darkness without adding expensive IR lighting systems reduces both hardware complexity and total cost of ownership.
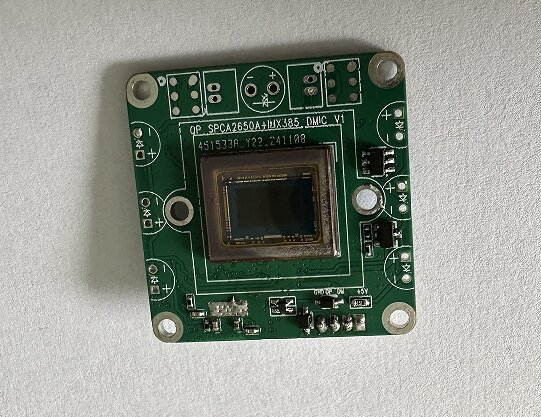
Another frequent request is: “Where can I find the IMX385 datasheet?” For engineers in the evaluation stage, access to precise technical documentation is crucial.
Search queries such as “IMX385 technical specifications” or “IMX385 camera module pinout” typically come from integrators designing circuit layouts or configuring firmware.
Recommendation: Beyond the datasheet, engineers benefit from ready-to-use IMX385 USB camera modules with standard UVC (USB Video Class) support. This allows plug-and-play operation on Windows, Linux, and ARM-based systems without needing custom drivers.
It is natural for engineers to benchmark the IMX385 against other popular sensors. Some of the most common comparisons include:
|
Sensor |
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
Best Use Cases |
|
IMX385 |
Exceptional low-light & starlight performance, larger pixels, STARVIS |
Lower resolution (2MP) compared to 4K sensors |
Night vision, industrial security, robotics |
|
IMX307 |
Cost-effective, good HD quality |
Slightly lower sensitivity than IMX385 |
Entry-level surveillance, IoT cameras |
|
IMX462 |
Extremely high NIR sensitivity, excellent night vision |
Limited resolution (2MP) |
AI vision, scientific imaging, IR-illuminated environments |
|
IMX415 |
4K UHD resolution, compact pixel design |
Smaller pixel size → weaker low-light compared to IMX385 |
High-resolution daytime monitoring, industrial detail capture |
When evaluating IMX385 vs IMX307, engineers find that the IMX385 offers stronger low-light results, while the IMX307 appeals to cost-sensitive projects. In IMX385 vs IMX462, the IMX462 wins in NIR-enhanced setups, but the IMX385 provides more balanced performance across natural night-light conditions. Against the IMX415 4K sensor, the IMX385 may sacrifice resolution, but delivers superior starlight performance.
Key takeaway: Engineers needing clear starlight-level imaging should prioritize the IMX385, especially for night vision industrial camera modules.
High-resolution sensors inevitably generate concerns around power and thermal management. Queries such as “IMX385 power consumption” and “IMX385 heat dissipation” highlight this.
Practical note: In surveillance deployments across European cities or U.S. warehouses, stable thermal performance ensures longer camera lifespan and fewer maintenance cycles.

Finally, engineers frequently ask: “How can I integrate the IMX385 into my project?” This involves both hardware and software considerations.
Conclusion: With proper SDK support and lens flexibility, integration is straightforward for robotics, industrial IoT, and smart surveillance.
Based on these five concerns, our Sony 1/2" IMX385 STARVIS Night Vision USB Camera Module offers engineers the best balance of low-light sensitivity, integration simplicity, and industrial reliability.
Q1. Can I use the IMX385 camera module in 24/7 surveillance?
A1. Yes. With optional metal housing for heat dissipation, it is optimized for continuous operation in smart city, factory, and logistics monitoring.
Q2. Does the IMX385 support Raspberry Pi or Jetson boards?
A2. Absolutely. The UVC compliance ensures seamless integration with SBC platforms for AI and robotics projects.
Q3. How does IMX385 compare to IMX415 in industrial vision?
A3. IMX385 excels in low-light and night vision, while IMX415 offers higher 4K resolution. Choose based on whether your project prioritizes clarity at night or ultra-high resolution in daytime.
Q4. What lens options are available for different applications?
A4. Wide FOV (2.8mm) for AMR navigation, mid-range (6mm) for general surveillance, and narrow (8mm) for detail inspection.
Q5. What industries benefit most from the IMX385 camera module?
A5. Robotics, industrial automation, logistics warehouses, smart city surveillance, and energy facility monitoring across the U.S. and Europe.
✅ Final Word:
For engineers and CTOs searching for IMX385 low light performance, IMX385 starlight vision, or IMX385 integration for industrial vision, the Sony IMX385 USB camera module with starlight lens options is a proven, future-ready solution.